

Some of the scalpel blade edges are coated with zirconium nitride which improves sharpness and edge retention. The scalpel blades are made of hardened and tempered steel, stainless steel, or high carbon steel. They are rigid and hence, do not bend easily. They are sharp and can penetrate evenly and make it easier to take a cut.ĥ. The surgical blades are fine enough and can make precise incisions.Ģ. This blade is used for making large incisions through thick skin. Number 22 blades: It is larger than the number 10 blade which has a curved cutting edge and flat unsharpened back edge. Number 15 blades: It has a small and curved cutting edge and is ideal for making short and precise incisions.ĥ. Number 12 blades: It is small, pointed and a crescent-shaped blade which is sharpened along the inside edge of the curve and used as a suture cutter.Ĥ. As it has a pointed tip it is an ideal blade for stab incisions and precise shortcuts in shallow recessed areas.ģ. Number 11 blades: Elongated and triangular blade.
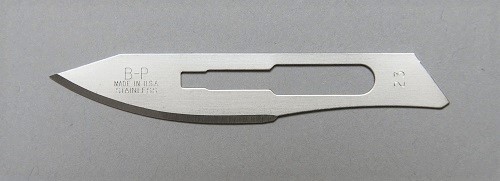
Used to make large incisions and cutting soft tissues.Ģ. Number 10 blades: It has a large cutting edge and one of the most traditional blades. The numbers for the surgical blades denote the size, shape and their particular use.ġ. There are some commonly used surgical blades and they have been distinguished as per numbers.

The disposable scalpels usually come with a plastic handle and an extensible knife and can be used only once.ĭuring surgery, the non-attached and replaceable blade is the most commonly used scalpel blade. The re-usable scalpel has permanently attached blades which can be re-used and also be sharpened. The surgical blades or scalpels can be single-use disposable or re-usable. The differentiating factor of surgical blades is the spine, slot, and edge. They have different numbers which indicate their size and shape.
Interleukin-10 reduces scar formation in both animal and human cutaneous wounds: results of two preclinical and phase II randomized control studies.A surgical blade is also known as the scalpel is an important tool for performing surgical procedures and tissue dissections. A plasma scalpel: comparison of tissue damage and wound healing with electrosurgical and steel scalpels. Effects of thermal knives on wound healing. Ancient technology in contemporary surgery. Comparison of wound-healing characteristics with feedback circuit electrosurgical generators in a porcine model. steel scalpel: a side by side comparison of cutaneous wound healing. Effects of steel scalpel, ultrasonic scalpel, CO2 laser, and monopolar and bipolar electrosurgery on wound healing in guinea pig oral mucosa. Surgical obsidian scalpel skin#
Comparative study of wound healing in rat skin following incision with a novel picosecond infrared laser (PIRL) and different surgical modalities. The ophthalmology microscalpel versus standard scalpels and wound healing in a rat model. A blinded histologic review suggested that obsidian wounds contained fewer inflammatory cells and less granulation tissue at 7 days. At 42 days, all wounds were barely detectable, thus precluding scar width analysis. At 21 days, scar width was not different in the two groups. Scar width, however, was significantly less in the obsidian wounds at 7, 10, and 14 days (p < 0.005). Tensile strength of the two wound types was not different at 7, 14, 21, and 42 days. Each rat received two parallel 8-cm dorsal skin incisions, one with an obsidian scalpel and the other with a surgical steel scalpel (no. In order to determine if skin incisions made with obsidian were superior to those made with standard surgical steel, wound tensile strength, scar width, and histology were assessed in 40 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. N2 - There are several anecdotal clinical articles claiming wound healing and scar superiority using obsidian (volcanic glass) scalpels. T1 - A comparison of obsidian and surgical steel scalpel wound healing in rats.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
